location
Get the global window.location object of the page that is currently active.
Syntax
cy.location()
cy.location(key)
cy.location(options)
cy.location(key, options)
Usage
Correct Usage
cy.location() // Get location object
cy.location('host') // Get the host of the location object
cy.location('port') // Get the port of the location object
Arguments
key (String)
A key on the location object. Returns this value instead of the full location object.
options (Object)
Pass in an options object to change the default behavior of cy.location().
| Option | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
log | true | Displays the command in the Command log |
timeout | defaultCommandTimeout | Time to wait for cy.location() to resolve before timing out |
Yields
cy.location() yields the location object with the following properties:
hashhosthostnamehreforiginpathnameportprotocolsearchtoString
When given a key argument:
cy.location()yields the value of the location property as a string
Examples
No Args
Make assertions about every location property
cy.visit('http://localhost:8000/app/index.html?q=dan#/users/123/edit')
cy.location().should((loc) => {
expect(loc.hash).to.eq('#/users/123/edit')
expect(loc.host).to.eq('localhost:8000')
expect(loc.hostname).to.eq('localhost')
expect(loc.href).to.eq(
'http://localhost:8000/app/index.html?q=dan#/users/123/edit'
)
expect(loc.origin).to.eq('http://localhost:8000')
expect(loc.pathname).to.eq('/app/index.html')
expect(loc.port).to.eq('8000')
expect(loc.protocol).to.eq('http:')
expect(loc.search).to.eq('?q=dan')
expect(loc.toString()).to.eq(
'http://localhost:8000/app/index.html?q=brian#/users/123/edit'
)
})
Check location for query params and pathname
We can yield the location object within a .should()
command and work with it directly.
cy.get('#search').type('niklas{enter}')
cy.location().should((loc) => {
expect(loc.search).to.eq('?search=niklas')
expect(loc.pathname).to.eq('/users')
})
Key
Assert that a redirect works
Grab only the pathname and add an assertion.
cy.visit('http://localhost:3000/admin')
cy.location('pathname').should('eq', '/login')
Notes
Native Location
No need to use window.location
Cypress automatically normalizes the cy.location() command and strips out
extraneous values and properties found in window.location. Also, the object
literal yielded by cy.location() is a basic object literal, not the special
window.location object.
When changing properties on the real window.location object, it forces the
browser to navigate away. In Cypress, the object yielded is a plain object, so
changing its properties will have no effect on navigation.
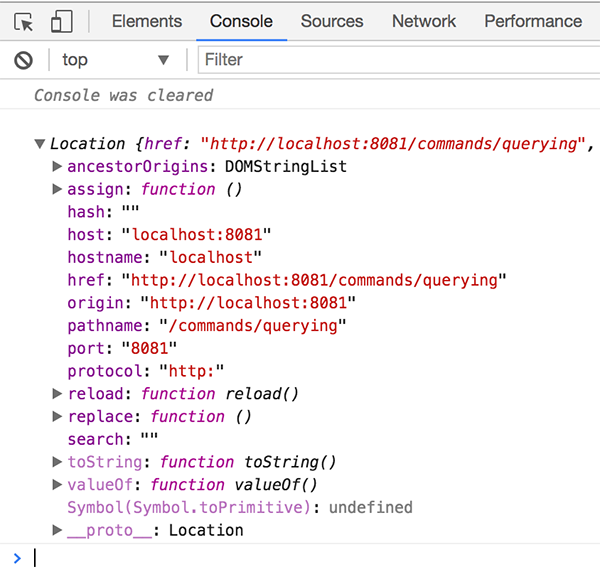
Console output of window.location
cy.window().then((win) => {
console.log(win.location)
})
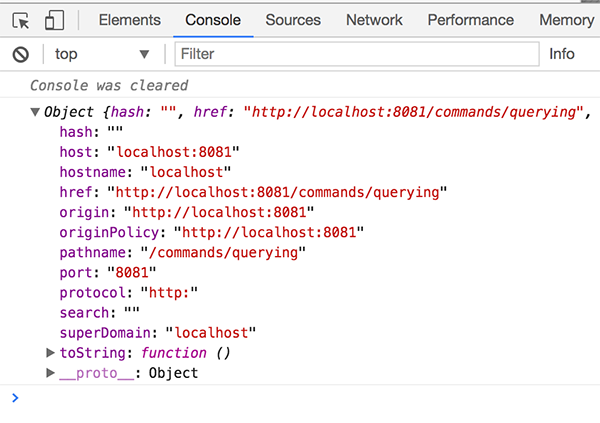
Console output of .location()
cy.location().then((loc) => {
console.log(loc)
})
Rules
Requirements
-
cy.location()requires being chained off ofcy.
Assertions
-
cy.location()will automatically retry until all chained assertions have passed
Timeouts
-
cy.location()can time out waiting for assertions you've added to pass.
Command Log
Assert on the location's href
cy.location().should((loc) => {
expect(loc.href).to.include('commands/querying')
})
The commands above will display in the Command Log as:
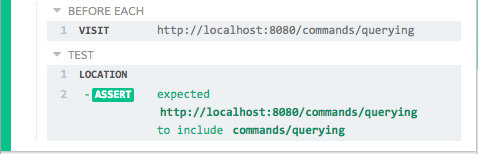
When clicking on location within the command log, the console outputs the
following: